WoT - Application Domains
WoT, as we already know, is a set of standards defined for the interoperability of different Internet of Things platforms and application domains by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It aims to preserve and complement existing IoT standards and solutions by providing a standardized approach for connecting and integrating smart devices, services, and applications into the Web.
In this section we will introduce some of the WoT application domains: Smart Homes, Industrial Applications, Agriculture, and Smart Cities.
Smart Homes
In smart homes, the ability to connect and manage multiple assets remotely over the network is highly beneficial.
This helps within various activities within the home, such as controlling lights, adjusting room temperature, managing home appliances, and enhancing security using smartphones. These capabilities enable optimization of energy and resource consumption.
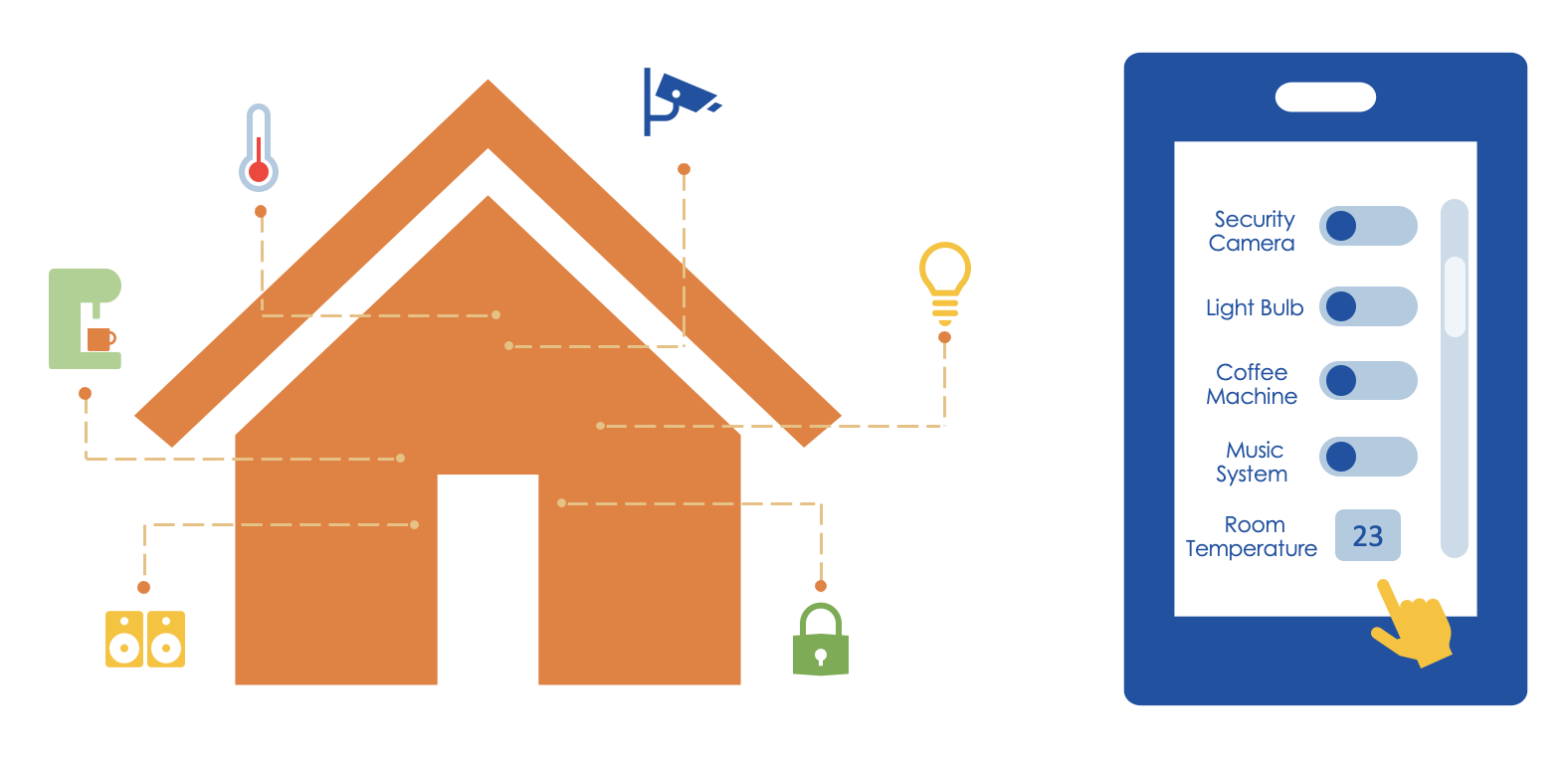
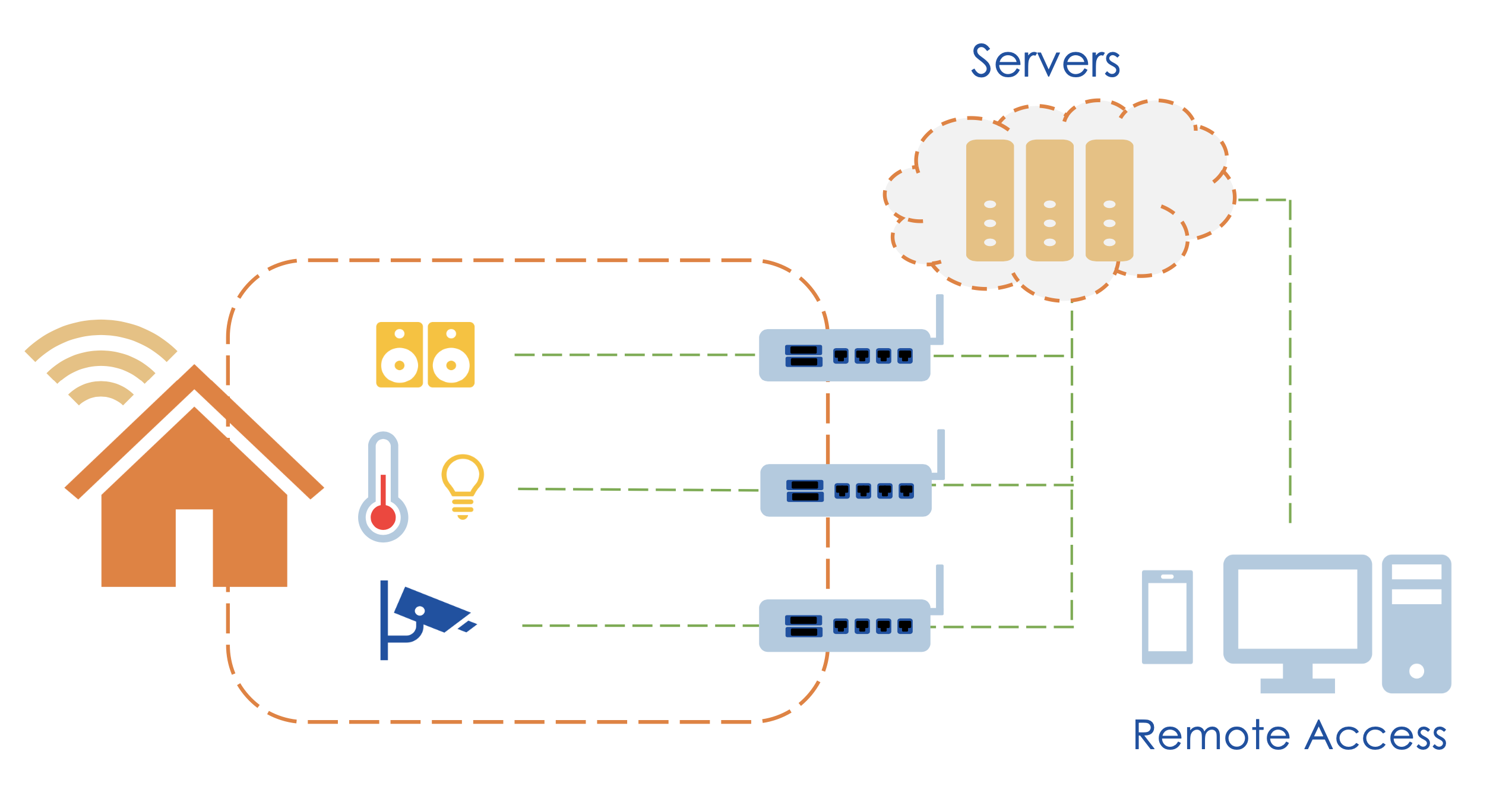
Let’s look at our smart home example closer. You can have direct remote access through gateway and routers, or interactions happen through an intermediary like a cloud application.
Services running in the cloud collect data from edge devices and provide the data to users of the smart home through edge devices such as phones or PCs.
Multiple edge devices are connected to the gateways through local communication protocols such as KNX, ECHONET, ZigBee, DECT ULE, and Wi-SUN. Multiple gateways can exist in one home, with each supporting multiple local protocols.
Industrial Applications
Industrial applications of WoT involve more complex use cases compared to smart homes. In factories, for instance, advanced monitoring of connected manufacturing equipment and products is essential, along with predictive maintenance to anticipate machine failures.
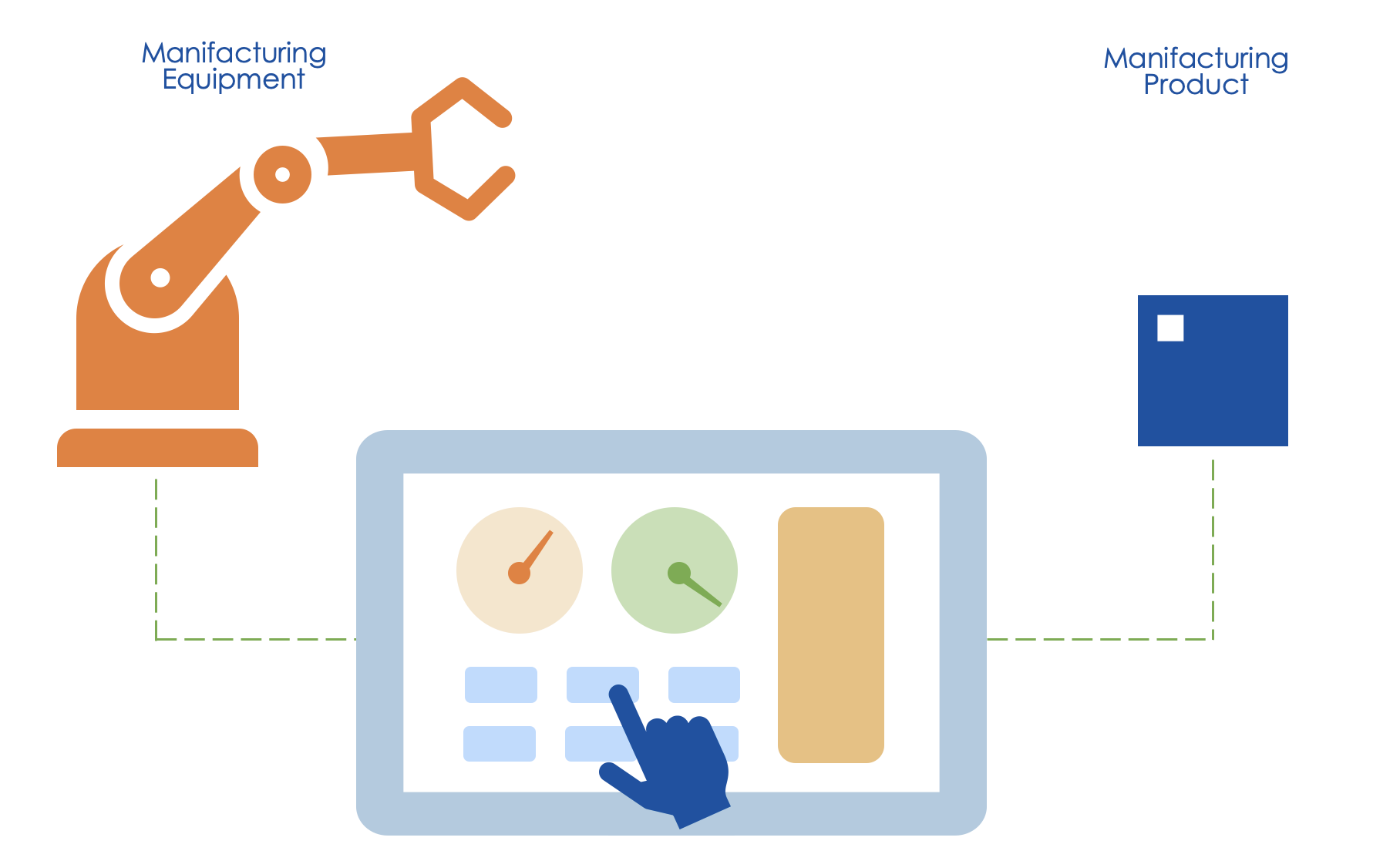
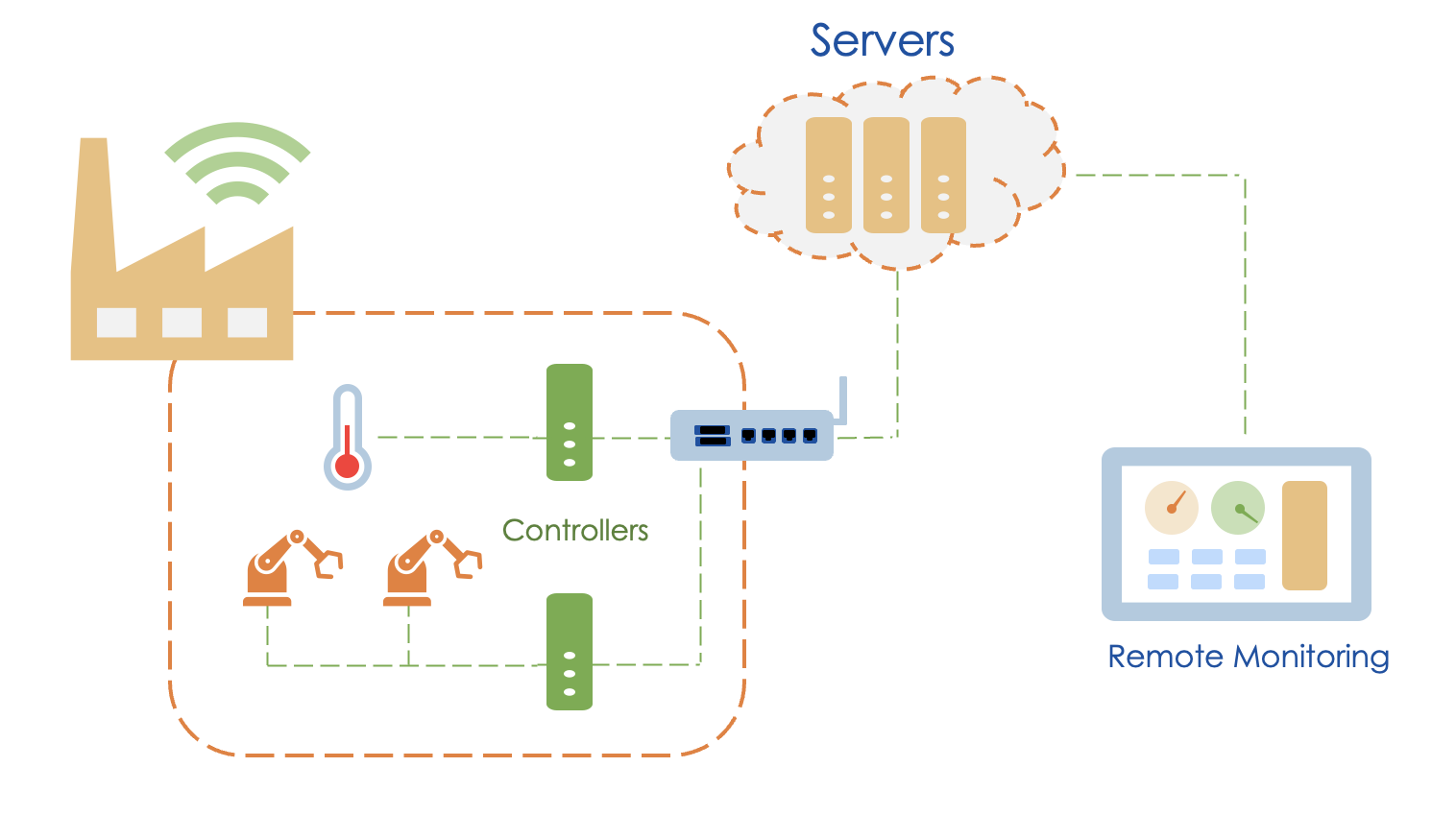
Let's look at one smart factory example in detail. Here, different factory equipment is automated based on industrial protocols such as PROFINET, Modbus, OPC UA TSN, EtherCAT, or CAN. Since industrial environments like factories, have more strict requirements, there are multiple controllers that are connected to the manufacturing equipment.
An industrial edge device collects data from various controllers and enables remote monitoring via a dashboard or analyzes it for preventative maintenance.
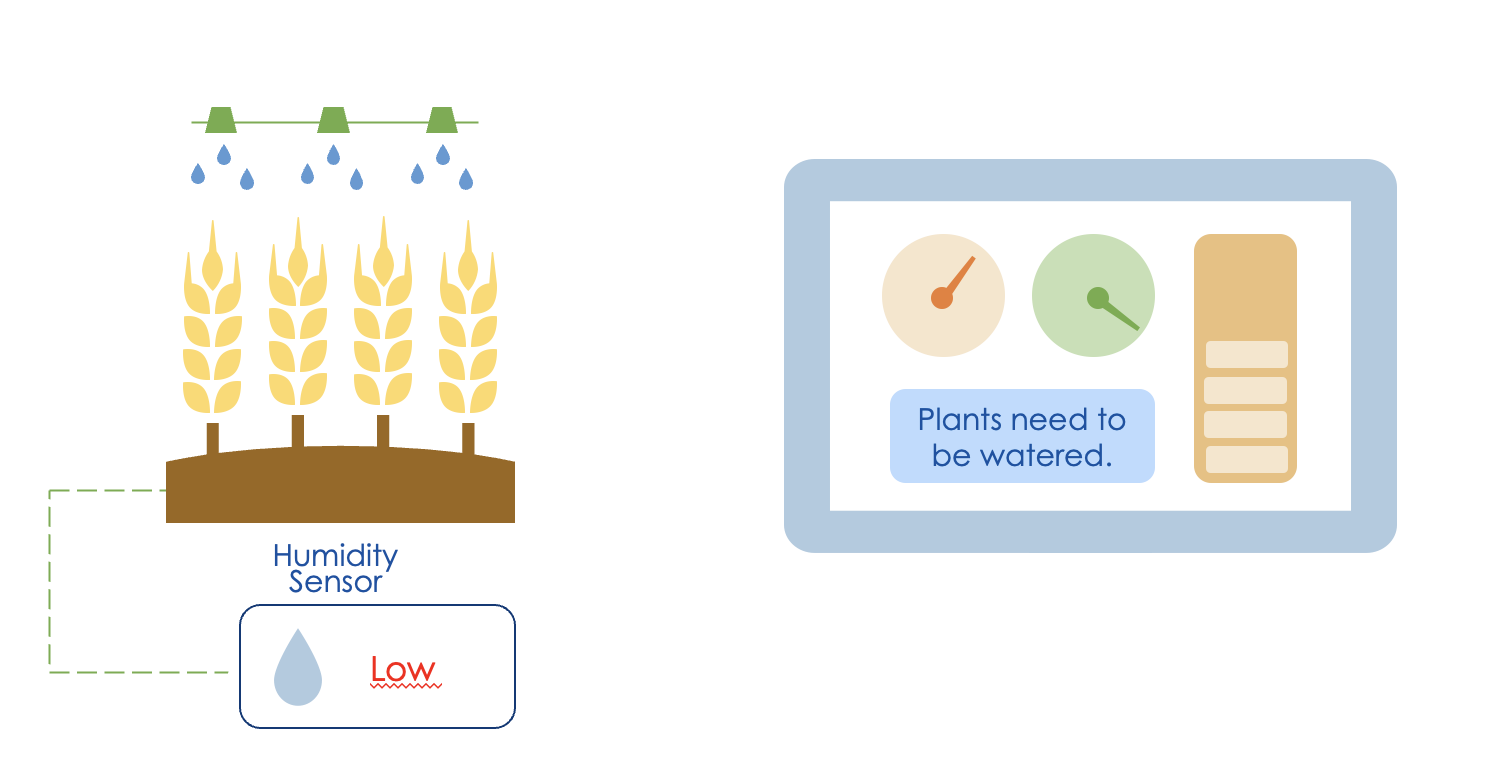
Agriculture Systems
Another domain-specific application is in agriculture systems.
With WoT, soil conditions can be monitored and optimal plans for watering and fertilizing can be created. Depending on the need, agricultural devices can be controlled remotely. Thus the quality and quantity of the harvest can be increased.
Smart Cities
The last application domain we will cover is smart cities. Similar to smart homes, monitoring of smart cities is possible. In this case, end users are citizens, municipalities, and government agencies.
In smart cities, bridges, dams, and canals can be monitored for material conditions or deterioration for maintenance repair work to prevent significant damage. Parking slots and street lights can be monitored for crowd management and optimized usage too.

What's More?
There are many more domain-specific examples in the WoT Architecture document besides the ones that we listed in this tutorial. If you want to learn more, you can refer to the WoT Architecture document available at: